Removal of a Fibroid Trapped in the Cervix or Falling Out of the Cervix
Fibroids inside the uterine cavity can sometimes be connected by a stalk (pedunculated submucous fibroid). Infrequently, the uterus contracts over time and pushes the fibroid into or through the cervical opening. This is called a prolapsed fibroid. These fibroids can usually be removed through the vagina without any abdominal incisions.
Symptoms- Women with a fibroid that has come through the cervix may have vaginal bleeding, watery vaginal discharge, constant menstrual-type cramping, vaginal pressure from the fibroid or no bothersome symptoms may occur.
Diagnosis – A prolapsed fibroid can usually be seen during a speculum examination and can be felt on the pelvic examination. A large cervical polyp can sometimes be confused with a fibroid. If the diagnosis is not clear, a pelvic MRI can help make the diagnosis and determine where the fibroid is attached to the uterus.
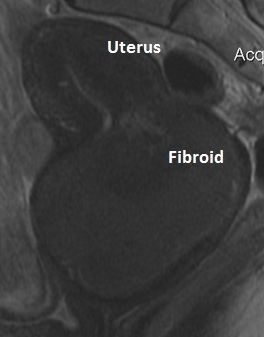
Fig: Fibroid Prolapsing through the Cervix and into the Vagina
Removing the Fibroid – The removal of a small, completely prolapsed fibroid can sometimes be performed in the office with local anesthesia or sedation. For removal of larger fibroids, women usually need anesthesia in an operating room. Pedunculated fibroids stuck inside the cervical canal can usually be removed in the operating room by making incisions in the cervix. Some women with pedunculated fibroids may require an abdominal myomectomy to remove it.
Risks – Complications of vaginal myomectomy for a prolapsed fibroid are rare. In two publications with 92 patients total, there were no complications. One potential complication of vaginal myomectomy is excessive bleeding from the fibroid site. This can be managed with a suture or with pressure to the bleeding site.
Results – The procedure is successful in most cases. In one publication, only 2 of 46 vaginal myomectomy procedures could not be completed, both because the gynecologist had difficulty reaching the fibroid stalk.
After Surgery – Women may have uterine cramping and/or vaginal spotting for a few days following vaginal myomectomy. If so, Tylenol of Aleve is usually adequate for pain relief. Women should call their doctor if fever, foul smelling vaginal discharge, or heavy bleeding occurs after surgery.
William H. Parker, MD
Clinical Professor, Reproductive Medicine, UC San Diego School of Medicine
Page last updated: January, 2018